Test-Driven Development (TDD) is a software development approach that emphasizes writing automated tests before writing the actual code. This methodology, initially proposed by Kent Beck in the late 1990s, has gained significant traction in the software development community due to its numerous benefits. Here we will delve into the intricacies of TDD, its advantages, and how to implement it effectively in your software development projects.
Understanding Test-Driven Development (TDD)
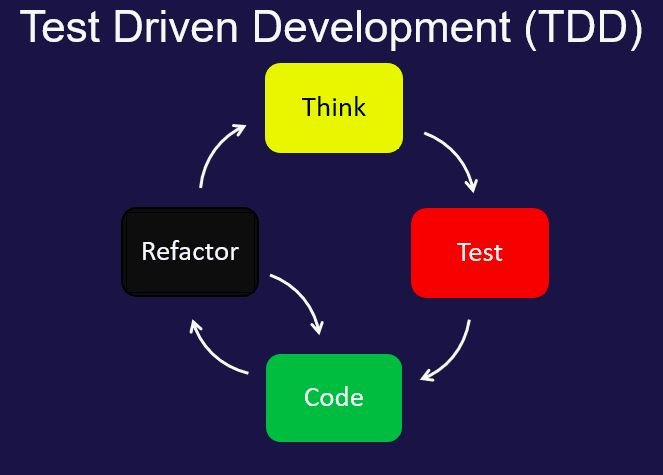
TDD is a software development methodology that revolves around the concept of writing tests before writing the code. This process ensures that the code is designed to pass the tests, thereby promoting a robust and maintainable software architecture. The primary steps involved in TDD are:
- Write a test case: Begin by writing a test that defines the desired functionality. The test should be specific, measurable, and achievable.
- Run the test: Execute the test to verify that it fails, as the code to fulfill the test’s requirements has not been written yet.
- Write the minimum code: Develop the smallest piece of code required to make the test pass.
- Refactor the code: Optimize the code to improve its readability, maintainability, and performance without altering its functionality.
- Repeat the process: Continue writing tests, making them pass, and refactoring the code until the entire functionality is covered.
Advantages of Test-Driven Development (TDD)
TDD offers several benefits to software developers and organizations, including:
Improved code quality: Writing tests before the code ensures that the software meets the desired specifications, leading to fewer defects and better overall quality.
Enhanced design: TDD encourages the creation of modular, loosely coupled, and highly cohesive code, which is easier to maintain and scale.
Reduced technical debt: By catching issues early in the development process, TDD minimizes the accumulation of technical debt, saving time and resources in the long run.
Better documentation: Test cases serve as an informal documentation of the software’s expected behavior, making it easier for new team members to understand the system.
Faster feedback: Automated tests provide immediate feedback on code changes, enabling developers to identify and fix issues quickly.
Implementing Test-Driven Development (TDD) in Your Projects
To successfully adopt TDD in your software development projects, consider the following best practices:
Start small: Begin by applying TDD to small, well-defined features or modules. As you gain experience and confidence, gradually expand its usage across the entire project.
Write expressive tests: Create test cases that are easy to understand, maintain, and debug. Use descriptive names and assertions to convey the intended functionality.
Keep tests independent: Ensure that each test is isolated from others, so the failure of one test does not affect the execution of others.
Maintain a high test coverage: Strive to cover all critical paths and edge cases in your tests to ensure comprehensive code coverage.
Collaborate with your team: Discuss and agree on the testing strategy with your team to ensure everyone is on the same page and can contribute effectively.
Common Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
While TDD offers numerous benefits, it also presents some challenges that teams must address:
- Initial resistance: Some team members may resist adopting TDD due to the perceived additional effort and time investment. Address this by highlighting the long-term benefits and providing training and support.
- Test maintenance: As the codebase evolves, tests may need to be updated to keep pace. Allocate time for regular test maintenance and refactoring to prevent this from becoming a burden.
- Test performance: Running a large suite of tests can sometimes be time-consuming. Use test isolation techniques and tools to optimize test execution speed without compromising test quality.
Tools and Technologies for Test-Driven Development (TDD)
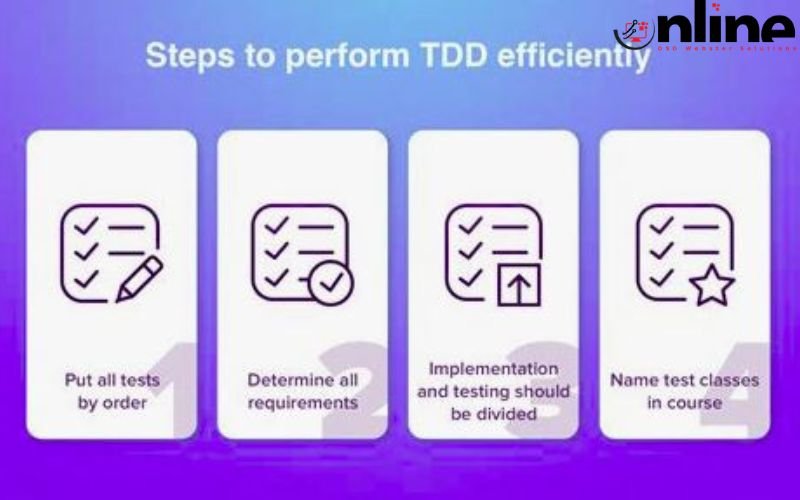
Numerous tools and technologies can facilitate the TDD process:
- Testing frameworks: Frameworks like JUnit (Java), pytest (Python), and xUnit (C#) provide the necessary infrastructure for writing and executing tests.
- Mocking and stubbing libraries: Libraries such as Mockito (Java) and Mockery (Python) help create test doubles to isolate dependencies during testing.
- Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) tools: Tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, and Travis CI automate the build, test, and deployment processes, ensuring that code changes adhere to TDD principles.
Final Thoughts
Test-Driven Development (TDD) is a powerful software development approach that promotes code quality, maintainability, and team collaboration. By understanding its principles, benefits, and best practices, you can effectively incorporate TDD into your software development projects and reap the rewards of a more robust and efficient development process.